Key takeaways
- What is demand forecasting? Demand forecasting provides the insight: a prediction of what customers will want, how much they’ll want, where they’ll want it, and when they’ll want it.
- What is demand planning? Demand planning turns that insight into action: strategies for procurement, production and inventory.
- How do demand forecasting and demand planning work together? Demand forecasting is the primary input into demand planning, which also incorporates inventory, capacity, and supply constraints. When integrated, the two deliver strategic clarity and operational excellence.
Supply chains run on a mix of prediction and execution. To stay competitive, businesses need to anticipate what customers will want while also having the operational ability to deliver on those expectations.
Here’s where demand forecasting and demand planning come in. While the two terms are often used interchangeably, they serve distinct yet complementary roles. Demand forecasting answers the “what” and “how much,” while demand planning addresses the “how” and “when.” Understanding the difference and how they work together is key to building a resilient, efficient and customer-focused supply chain.
What is demand forecasting?

Demand forecasting is the process of estimating future customer demand using data, statistical models and market insights. At its core, it is predictive. Businesses look at historical sales, seasonal trends, external signals and in many cases, machine learning algorithms to anticipate what customers will buy and when.
There are several methods companies use, depending on their industry and complexity:
- Time-series models, such as moving averages or exponential smoothing, are used to identify recurring patterns and seasonality
- Causal models like regression analysis link demand to external drivers such as economic conditions or promotions
- Qualitative methods, such as expert judgment or market research, are often used when historical data is limited
- AI and machine learning models that analyze large volumes of structured and unstructured data to improve accuracy and adapt to real-time changes
The goal is not just to generate numbers, but to build a reliable picture of expected demand. This forecast becomes the foundation for procurement decisions, production scheduling, workforce planning and financial projections. Without it, companies risk overcommitting resources or failing to meet customer needs.
By answering “what will customers want and how much?”, demand forecasting provides the critical input every supply chain relies on.
What is demand planning?

Demand planning is the process of taking demand forecasts and turning them into actionable strategies across the supply chain. Where forecasting provides the numbers, planning answers the question: “How will we meet that demand?”
It is broader and more strategic than forecasting, because it integrates multiple business functions and operational realities. Demand planning accounts for supplier capacity, production constraints, inventory levels, logistics and even financial goals. The process is collaborative, often involving sales, operations, finance and procurement teams to align around a unified plan.
Key elements of demand planning include:
- Inventory planning to ensure stock levels meet demand without tying up excess capital
- Procurement planning to align supplier orders with projected needs
- Production planning to schedule manufacturing efficiently while minimizing downtime or waste
- Logistics planning to coordinate distribution and delivery in line with customer expectations
When forecasts are combined with real-world constraints, demand planning ensures businesses can respond to market needs with agility and precision. It shifts the focus from prediction to execution, aligning every part of the supply chain toward meeting customer demand profitably and reliably.
What are the core differences between demand forecasting and demand planning?
Purpose & scope
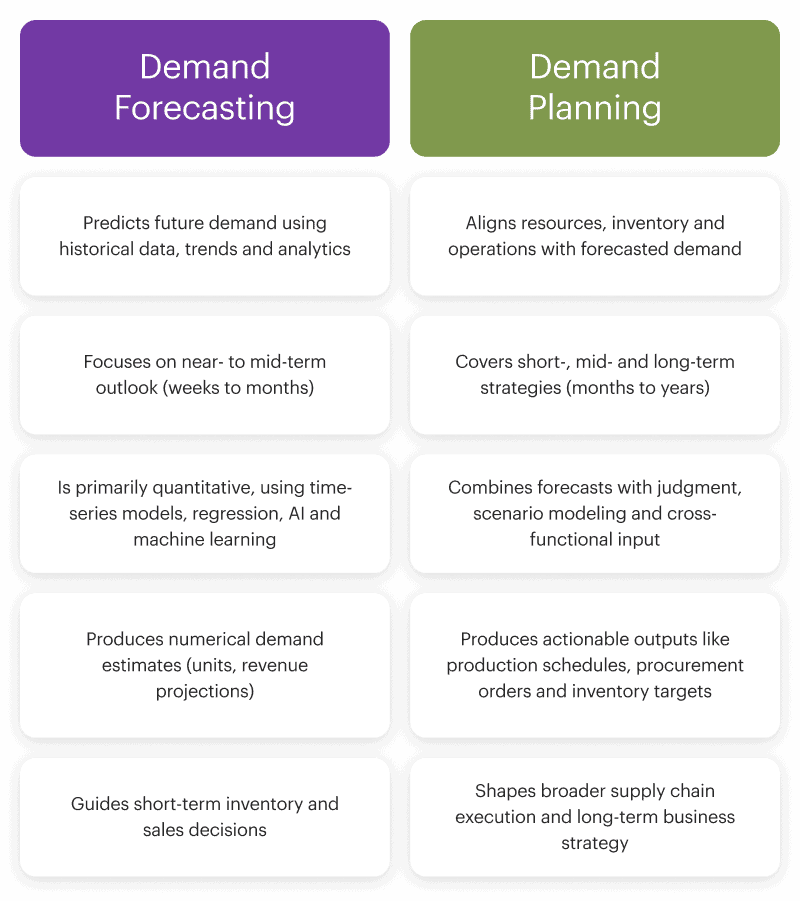
The primary purpose of demand forecasting is to predict what customers will want in the future. It focuses on creating a data-driven estimate of market demand. Demand planning, by contrast, takes that prediction and expands its scope to include how the business will respond. It turns insight into coordinated action across procurement, production, inventory and logistics.
Time horizon
Forecasting typically looks at the near- to mid-term, often ranging from weeks to a year, depending on the industry. Its focus is on generating timely insights that reflect expected demand shifts. Planning covers a wider spectrum. It includes short-term execution like daily production schedules, mid-term activities such as quarterly procurement and long-term strategies like capacity investments.
Methodologies
Forecasting relies on analytical techniques like time-series models, regression and increasingly AI-driven methods to generate demand estimates. Planning uses those forecasts as a starting point, but also incorporates business judgment, scenario modeling and cross-functional coordination. In this way, planning balances quantitative inputs with qualitative considerations and operational realities.
Output
The output of forecasting is a numerical estimate of demand, often expressed in units or revenue projections. These figures guide high-level expectations but stop short of defining action. The output of planning is more concrete: production schedules, procurement orders, inventory targets and logistics plans. Together, the two ensure both clarity of demand and the capability to fulfill it.
Visual comparison: planning vs. forecasting
Why both are crucial: the synergy in supply chain management
Demand forecasting and demand planning are strongest when they work in tandem. Forecasting provides a clear picture of likely demand, while planning transforms that insight into coordinated action across the supply chain. Without forecasting, demand planning lacks a reliable foundation. Without planning, demand forecasting becomes an academic exercise with little business impact.
Companies that connect forecasting and planning gain measurable advantages, such as:
- Fewer stockouts
- Lower excess inventory
- Better use of working capital
- Stronger customer satisfaction
Together, these functions build resilience and position businesses to compete in fast-changing global markets.
Ready to turn insight into action?
E2open connects forecasting and planning on one integrated platform, giving you the visibility, intelligence and agility to respond to demand with confidence.
Emerging trends in forecasting and planning
The way companies forecast and plan demand is evolving quickly. Advances in analytics and technology, along with rising customer expectations, are reshaping how supply chains operate. Three trends stand out:
The role of AI and machine learning
AI and machine learning are making forecasts more accurate by uncovering patterns that traditional models miss. From sales history to external signals like weather or economic indicators, they process massive datasets to generate smarter predictions. Just as important, they enable real-time adjustments, so forecasts are never static but constantly improving.
Demand sensing and responsive planning
Traditional forecasting often relies on monthly or quarterly cycles, but markets move faster. Demand sensing uses real-time data streams such as point-of-sale transactions, social media sentiment or shipment updates to refine forecasts daily or even hourly. Responsive planning takes those signals and adapts supply chain strategies on the fly, allowing companies to pivot quickly when demand shifts.
Strategic integration with S&OP
Demand planning is increasingly tied to Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) processes. By integrating forecasts and plans into cross-functional alignment, companies connect supply chain execution with broader business objectives. This ensures finance, sales, operations and supply teams are working toward a unified plan rather than operating in silos.
Business benefits of aligning forecasting and planning
When demand forecasting and demand planning are connected, the supply chain becomes more accurate, agile and resilient. Instead of operating on isolated predictions or fragmented execution, businesses move in step with both market signals and operational realities. The benefits are measurable:
- Reduced stockouts and overstocks: Companies avoid missed sales from underestimating demand while minimizing excess inventory that ties up working capital.
- Optimized production planning: Manufacturing schedules align more closely with real demand, reducing downtime and costly changeovers.
- Lower carrying and logistics costs: Better synchronization across procurement, warehousing, and transportation prevents unnecessary storage and rush shipments.
- Improved customer service: Reliable product availability leads to higher service levels and stronger customer loyalty.
- Greater resilience and agility: With integrated forecasting and planning, businesses can pivot quickly when disruptions arise, whether from supply shocks, market volatility, or sudden demand shifts.
Ultimately, aligning these functions transforms forecasting from a static prediction into a driver of operational excellence. It’s the difference between knowing what’s coming and being prepared to deliver against it.
Unlock smarter planning with e2open
Aligning demand forecasting and demand planning is powerful on its own. With e2open, you can take that integration even further. The platform connects forecasts with real-time end-to-end supply chain execution, giving your business:
- End-to-end visibility into demand signals, supplier capacity and logistics constraints
- AI-powered insights that continuously improve forecast accuracy and adapt plans in real time
- Cross-functional collaboration tools that bring sales, operations, and finance into alignment on one platform
When insight and action come together in a single connected environment, your business is equipped to reduce risk, capture opportunities faster and operate with confidence in any market condition.
Learn more about how e2open can help you plan and manage your supply chain with confidence.




